
"Ring of Fire" Solar Eclipse on October 14, 2023 Everything you need to know
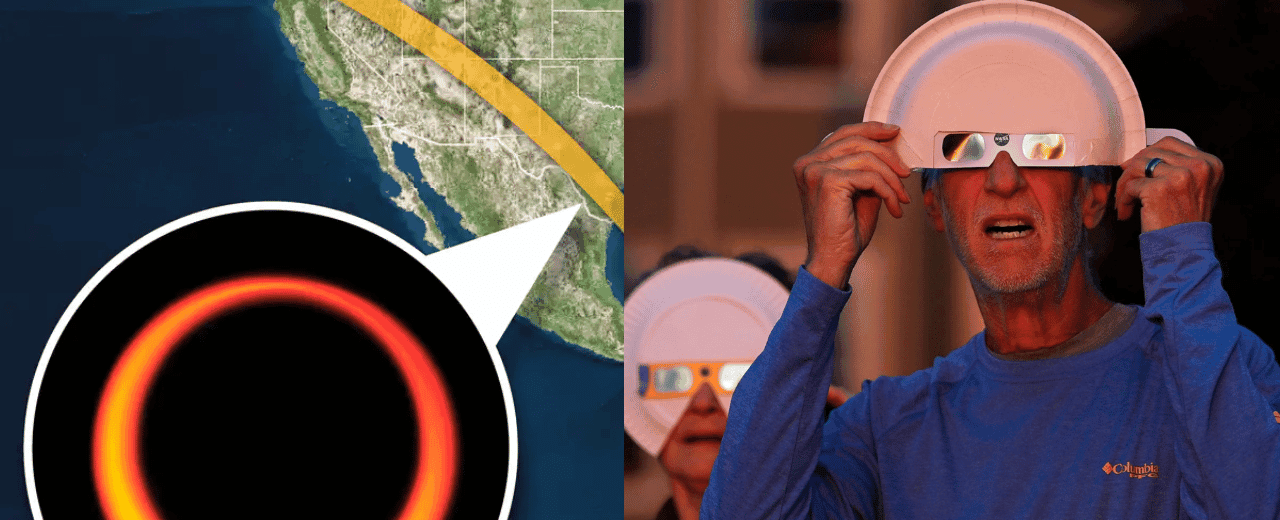

Table Of Contents
Solar eclipses have been a subject of fascination for people from all over the world since ancient times. These events have been interpreted in different ways by different cultures throughout history. Some cultures believe that solar eclipses represent the anger of gods, some use them to predict future events, and others organize elaborate festivals to celebrate them.
On October 14, 2023, a spectacular total solar eclipse will occur, drawing the attention of skywatchers across the globe to the American continent. The eclipse path will start in the Pacific Ocean, and will touch the Atlantic Ocean by traveling through North and South America.
Solar eclipses are rare astronomical events that only occur when the Moon comes in between the Sun and the Earth. This natural phenomenon results from the Sun, Moon, and Earth aligning precisely, allowing the Moon to cast a shadow on the Earth’s surface. Depending on the position of the Moon at these crossings and the way the inhabitants of the Earth see it, the eclipses can be categorized as Total, Partial, or Annular.
Annular Solar Eclipse
An annular solar eclipse occurs when the Moon is at its farthest point from the Earth during a solar eclipse, resulting in the Moon appearing smaller than the Sun in the sky. As a result, a thin ring of sunlight is visible around the edges of the Moon, creating a stunning sight for onlookers. Annular eclipses are a rare astronomical phenomenon, unique from other types of eclipses such as total and partial eclipses. Unlike a total solar eclipse, where the Moon completely covers the Sun, an annular eclipse only partially covers it, resulting in the perfect ring of fire around the edges. If you’re lucky enough to witness an annular eclipse in person, it’s an experience that you’ll never forget.
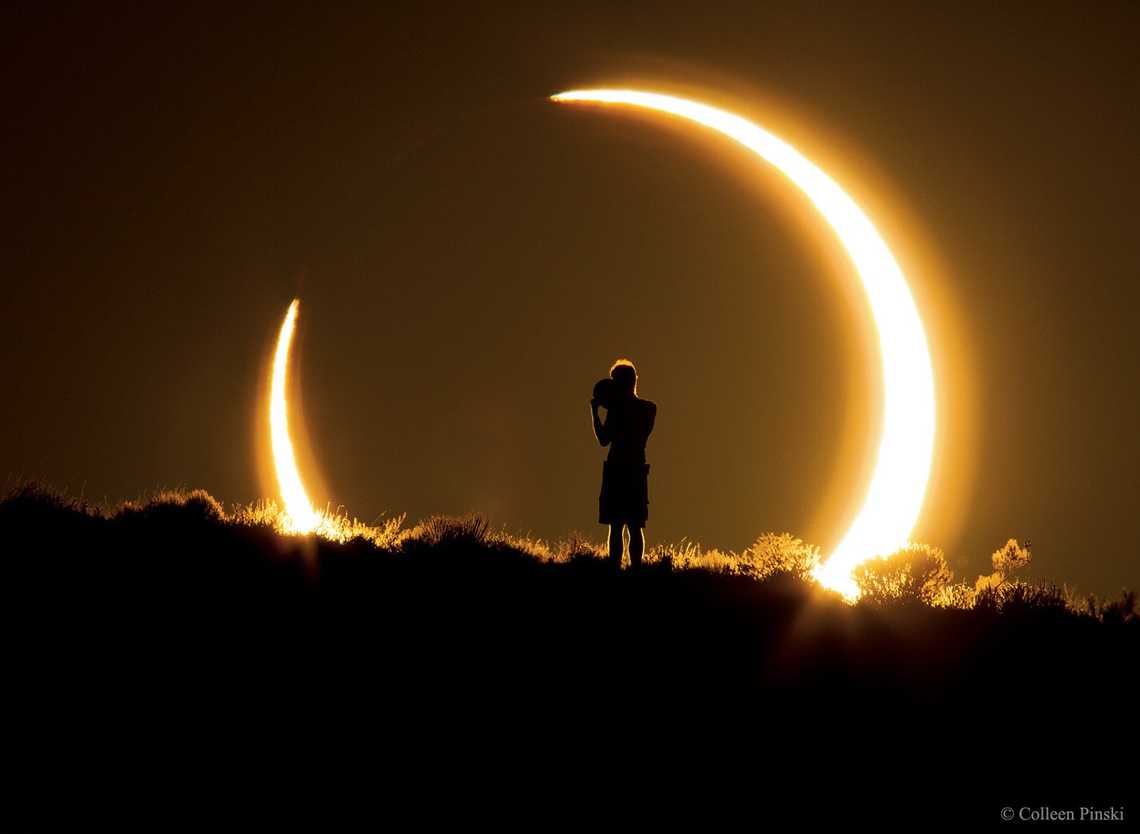

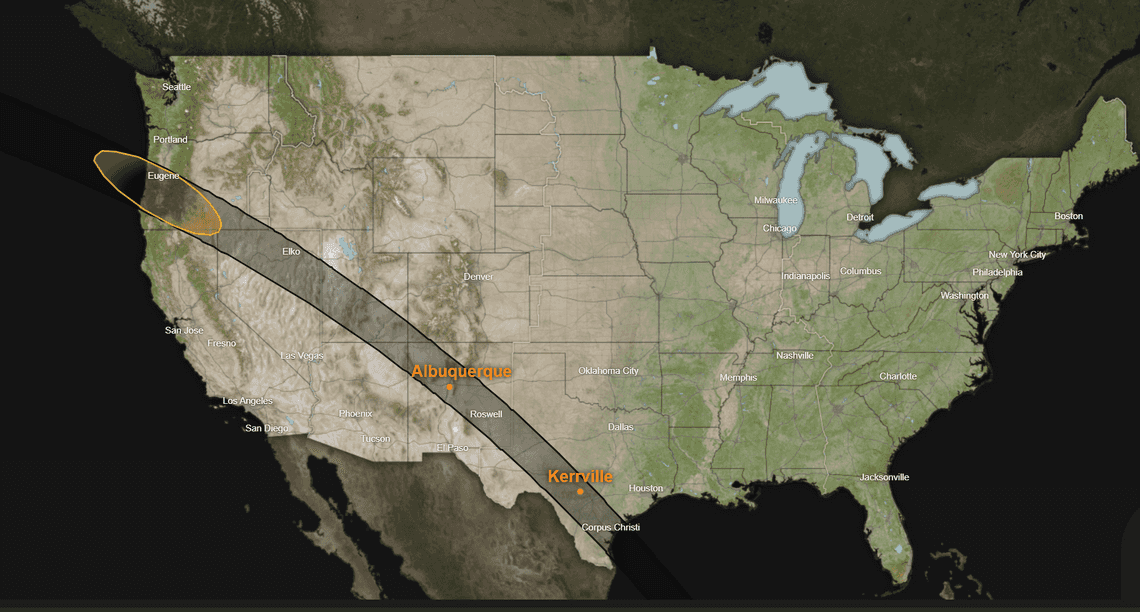
Annular Solare Eclipse on 14th October 2023
This annular eclipse can be viewed from the USA🇺🇸, followed by parts of Mexico🇲🇽, Central America, Colombia🇨🇴, and Brazil🇧🇷. The phenomenon of annularity, where the Sun forms a ‘ring of fire’ around the Moon, will be visible along a narrow path crossing the USA from Oregon to Texas. This path then extends over Mexico’s Yucatán peninsula, touching parts of Belize🇧🇿, Guatemala🇬🇹, Honduras🇭🇳, Nicaragua🇳🇮, Costa Rica🇨🇷, Panama🇵🇦, Colombia, and Brazil. Beyond these regions, a partial eclipse will grace the skies for observers located anywhere in the Americas—from Alaska🇺🇸 to Argentina🇦🇷.
How to observe a solar Eclipse
First things first: Never look directly at the sun during a solar eclipse, even during the partial phases.
It is important to remember that the sun is always very bright, even during a solar eclipse. Looking directly at the sun can damage your eyes and cause permanent vision loss. The only safe way to view a solar eclipse is to use certified eclipse glasses or a solar filter.
Viewing tips:
Use certified eclipse glasses: These glasses are designed to protect your eyes from the sun’s harmful rays during a solar eclipse. Using regular sunglasses or homemade devices can cause permanent damage to your eyes.

Never look directly at the sun, even during a partial eclipse, without proper eye protection. Use a telescope or binoculars with caution: Looking directly at the sun through a telescope or binoculars can also damage your eyes. Use filters that are specifically designed for solar viewing and always cover the finder scope with the appropriate filter.

1. Use a telescope or binoculars with caution: Looking directly at the sun through a telescope or binoculars will damage your eyes.
Solar eclipses are rare and awe-inspiring events that can only be seen from a small portion of the Earth’s surface. But if you’re lucky enough to live in a path of totality/annularity, or even a partial eclipse, don’t miss the chance to experience it!
Related Posts



